















Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
Smart and Sustainable Agriculture: Revolutionizing the Farming Industry

With the world population growing at an exponential rate, the demand for food is also on the rise. To meet this increasing demand, the agriculture industry needs to evolve and adapt to new technologies and practices that can ensure sustainable and efficient production. Smart and sustainable agriculture is the answer to these challenges, revolutionizing the way we farm and paving the way for a more secure and resilient food system.
The Concept of Smart and Sustainable Agriculture
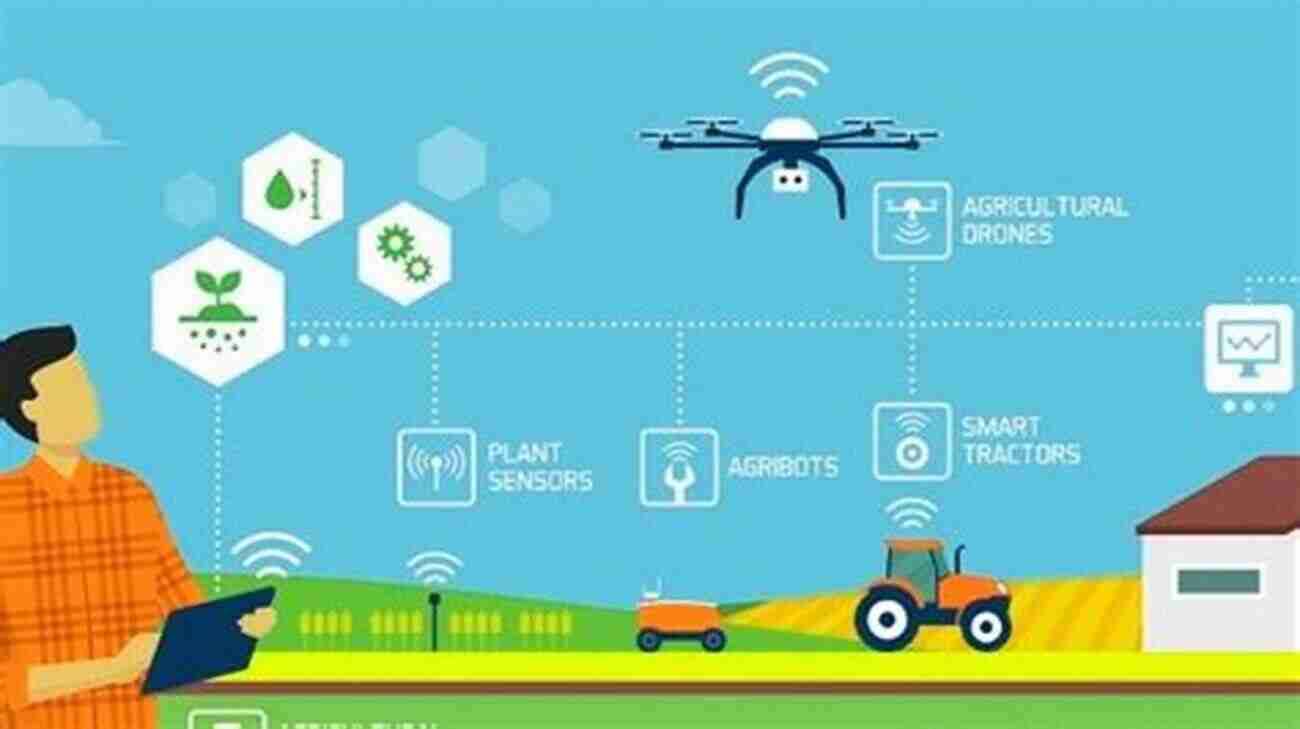
Smart agriculture refers to the use of modern technologies such as sensors, robotics, drones, and Artificial Intelligence (AI) in farming practices. These technologies enable farmers to make data-driven decisions, optimize resource usage, streamline processes, and improve overall productivity. By harnessing the power of these innovations, farmers can produce higher yields with minimal environmental impact.
Sustainable agriculture, on the other hand, focuses on preserving natural resources, minimizing waste, and ensuring the long-term viability of farming systems. It incorporates methods like organic farming, crop rotation, precision agriculture, and integrated pest management, to name a few. The objective is to minimize the environmental footprint of agriculture while maintaining economic viability.
4.8 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 28875 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Word Wise | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 336 pages |
The Benefits of Smart and Sustainable Agriculture
By embracing smart and sustainable agriculture practices, farmers can unlock a multitude of benefits:
Increased Efficiency
The integration of smart technologies allows farmers to optimize their resource usage. Sensors can monitor soil moisture levels, plant health, and nutrient requirements, enabling targeted application of water and fertilizers. Drones equipped with imaging and mapping capabilities can identify areas that need attention, improving overall efficiency and reducing waste.
Enhanced Productivity
Smart technologies enable farmers to collect and analyze vast amounts of data, leading to better decision-making. By leveraging AI algorithms, farmers can identify patterns, predict outcomes, and implement appropriate measures to maximize yield. This data-driven approach helps optimize crop growth, minimize disease outbreaks, and increase overall productivity.
Reduced Environmental Impact
Sustainable farming practices contribute to preserving soil health, water quality, and biodiversity. Precision agriculture techniques minimize the use of synthetic inputs, decreasing the potential for pollution and soil degradation. Organic farming eliminates the use of harmful pesticides and promotes natural pest control mechanisms, resulting in safer food production and healthier ecosystems.
Improved Resilience
Smart technologies empower farmers to better adapt to climatic changes and unforeseen events. By monitoring weather patterns and soil conditions in real-time, farmers can make informed decisions about planting, irrigation, and harvesting. This ability to adapt quickly increases the resilience of farming systems to climate shocks and ensures a more reliable food supply.
Examples of Smart and Sustainable Agriculture Solutions
The adoption of smart and sustainable agriculture practices is gaining momentum worldwide. Let's explore a few examples:
Vertical Farming
Vertical farming involves the cultivation of crops in vertically arranged layers, often in urban environments. By utilizing hydroponics or aeroponics systems, vertical farms can operate efficiently with significantly less water compared to traditional farming methods. LED lighting and automated nutrient delivery systems optimize plant growth, allowing year-round production of fresh and nutritious crops.
Precision Livestock Farming
Precision livestock farming relies on sensor technologies to monitor animal health, behavior, and productivity. Sensors placed on animals can provide early detection of diseases or abnormalities, allowing for timely intervention and improved animal welfare. The data collected can also help optimize animal nutrition, reduce the environmental impact of livestock farming, and minimize the use of antibiotics.
Smart Irrigation Systems
Water scarcity is a significant concern in agriculture. Smart irrigation systems help farmers optimize water usage by monitoring soil moisture levels and weather conditions. By delivering water precisely where and when it is needed, excessive wastage is minimized, leading to increased water efficiency and reduced energy consumption.
Robotics and Automation
The use of robots and automation in farming operations can reduce labor-intensive tasks, increase efficiency, and minimize errors. Autonomous robots can perform activities such as planting, weeding, and harvesting with precision and speed. This technology not only saves time and labor costs but also reduces the need for chemical herbicides and pesticides.
Overcoming Challenges and Promoting Adoption
Although smart and sustainable agriculture holds immense potential, there are challenges to overcome for widespread adoption:
Cost of Technology
The initial investment in smart technologies can be a barrier for small-scale farmers. Governments and organizations need to provide financial incentives and support to make these technologies more accessible, enabling a wider range of farmers to adopt them.
Education and Training
Farmers need to be educated and trained on the concepts and implementation of smart and sustainable agriculture. Providing workshops, training programs, and access to educational resources can ensure that farmers have the necessary knowledge and skills to embrace these innovative practices.
Infrastructure and Connectivity
Rural areas, where agriculture is often practiced, may lack sufficient internet connectivity and infrastructure to support smart technologies. Governments and private sectors should invest in improving connectivity and establishing an infrastructure framework that enables the seamless integration of smart agricultural solutions.
The Future of Farming
Smart and sustainable agriculture has the potential to transform the farming industry, addressing the challenges of food security, climate change, and resource scarcity. By combining advanced technologies, environmental stewardship, and data-driven decision-making, farmers can create a more resilient, productive, and sustainable food system.
The future of farming lies in the hands of those willing to embrace innovation and work towards a sustainable future. Through collaboration, investment, and knowledge sharing, we can build a smarter and more sustainable agriculture industry that ensures food security while protecting our planet for future generations.
4.8 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 28875 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Word Wise | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 336 pages |
This book constitutes the refereed proceedings of the First International Conference on Smart and Sustainable Agriculture, SSA 2021, held as a virtual event in June 2021.
The 12 papers presented were thoroughly reviewed and selected from the 25 qualified submissions. The papers provide discussion on new trends in communication and networking, Internet of Things, data processing for smart agriculture, renewable-energy based devices, low-cost solutions for wide-area exploitations and developing countries, smart agriculture and urban farming, smart irrigation, application to small-size andlarge-size exploitations, application of ancestral farming to smart agriculture, waste management for agriculture 2.0, and census of regional ancestral farming.

 Calvin Fisher
Calvin FisherThe Most Insightful and Liberating Experiences Found in...
When it comes to expanding our...

 D'Angelo Carter
D'Angelo CarterDax To The Max Imagination: Unlock the Power of...
Welcome to the world of Dax To...

 Chris Coleman
Chris ColemanThe Hidden Case of Ewan Forbes: Uncovering the Mystery...
Ewan Forbes: a...

 Morris Carter
Morris CarterWhen Newport Beat New Zealand: A Historic Rugby Upset
The rivalry between Newport and New Zealand...

 David Mitchell
David MitchellThe Soul of an Astronomer: Women of Spirit
Astronomy, the study of...

 Ethan Gray
Ethan GrayThe Military Origins Of The Republic 1763-1789
When we think about the birth of the...

 Guy Powell
Guy PowellRPO System for 10 and 11 Personnel: Durell Fain
When it comes to...

 Evan Hayes
Evan HayesMadness: The Ten Most Memorable NCAA Basketball Finals
College basketball fans eagerly await the...

 Jorge Amado
Jorge AmadoDiscover the Magic of Polish: English First 100 Words,...
Are you ready to embark on a linguistic...

 Shaun Nelson
Shaun NelsonUnlock the Secrets of Edwidge Danticat's Breath, Eyes,...
Are you delving into the world...

 Walt Whitman
Walt Whitman300 Years Liechtenstein: The Birth of Fish Out of Water...
Once upon a time, in the...

 Jaden Cox
Jaden CoxExploring the Legendary Surfers of Early Surfing in the...
Surfing, a sport...
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!
 Jeffery BellFollow ·18.6k
Jeffery BellFollow ·18.6k Ernesto SabatoFollow ·16.6k
Ernesto SabatoFollow ·16.6k Jamie BlairFollow ·14.5k
Jamie BlairFollow ·14.5k Andres CarterFollow ·14.1k
Andres CarterFollow ·14.1k Rob FosterFollow ·2k
Rob FosterFollow ·2k Andy HayesFollow ·2.9k
Andy HayesFollow ·2.9k Vladimir NabokovFollow ·8.3k
Vladimir NabokovFollow ·8.3k J.D. SalingerFollow ·3.5k
J.D. SalingerFollow ·3.5k