

















Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
The State In Ancient Egypt: Exploring the Rulers and Administration of an Ancient Civilization
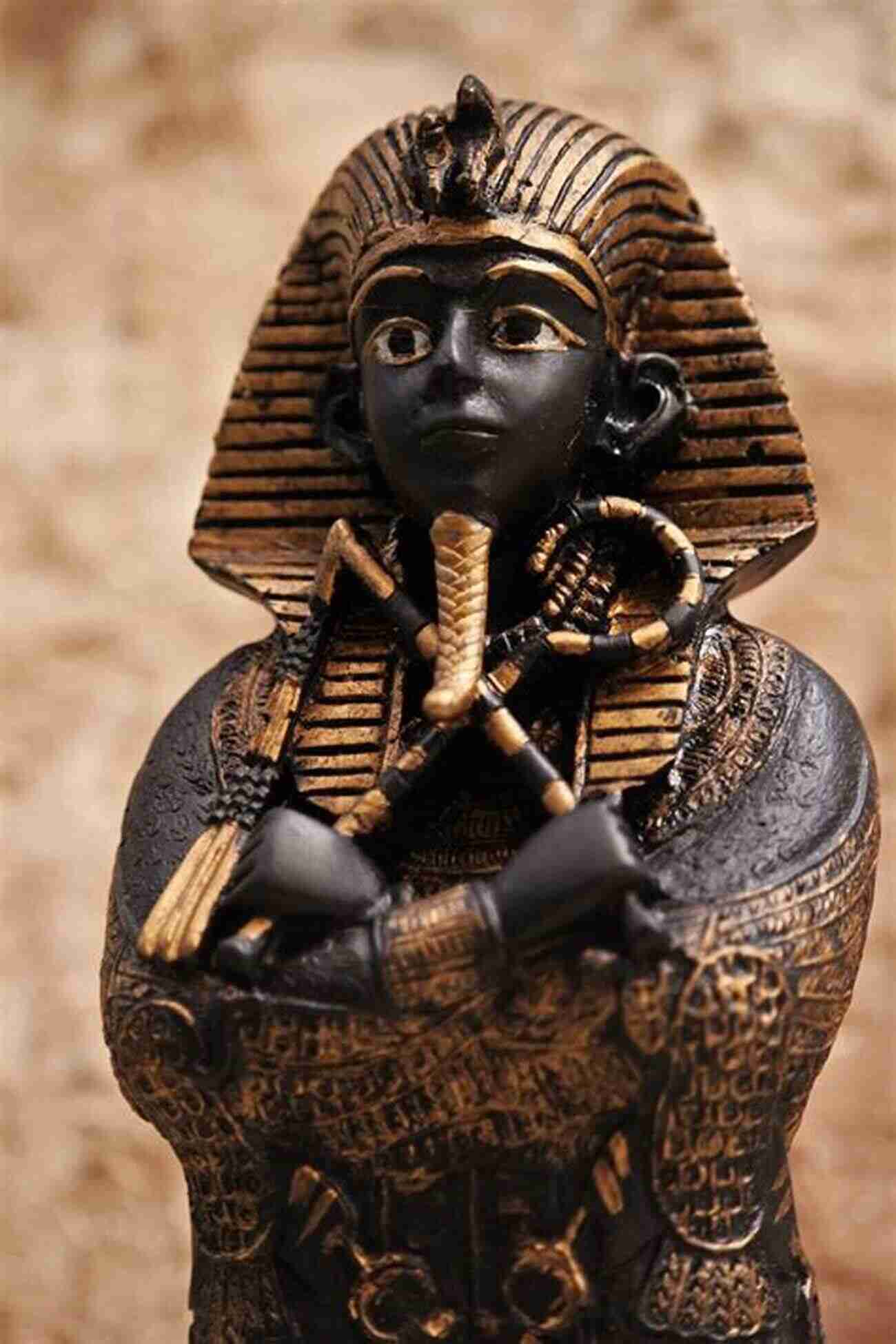


Ancient Egypt, one of the world's oldest civilizations, thrived for over three millennia, leaving behind a rich legacy of cultural and architectural wonders. At the heart of this magnificent empire was a complex administrative system that ensured seamless governance. In this article, we will delve into the state structure, rulers, and administration of ancient Egypt, shedding light on the secrets that enabled this civilization to prosper.
1. Pharaohs: The Divine Rulers
The pharaohs, believed to be the living embodiment of gods on earth, were at the apex of the ancient Egyptian state. Thousands of years of dynastic rule shaped the civilization, with each pharaoh considered the ultimate authority. Their reigns were marked by both grandeur and challenges, as they governed a vast empire with wisdom and divine guidance.
These titans of ancient Egypt dedicated their lives to upholding justice and ma'at (balance and order). Their magnificent tombs, such as the iconic Pyramids of Giza, stand as testament to their immense power and the perceived connection between their mortal existence and the afterlife.
4.8 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 4520 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Word Wise | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 220 pages |
| X-Ray for textbooks | : | Enabled |
2. Government Structure: Maintaining Order and Prosperity
The Egyptian government functioned as a centralized bureaucracy, with various departments and officials responsible for different aspects of governance. At the top of the hierarchy was the pharaoh, who held absolute authority.
Below the pharaoh, a group of trusted nobles and high-ranking officials formed the royal court. They assisted the pharaoh in decision-making and oversaw the various administrative departments. This inner circle included priests, viziers, and army commanders.
The country was divided into administrative divisions known as nomes, each governed by a nomarch. The nomarch was responsible for collecting taxes, maintaining law and order, and overseeing local infrastructure projects.
3. The Role of Viziers: The Hand of the Pharaoh
The vizier held a pivotal role in the ancient Egyptian government. Appointed by the pharaoh, the vizier served as the chief minister and right-hand to the ruler. This prestigious position required exceptional administrative skills, as the vizier managed the day-to-day affairs of the state.
The vizier supervised the treasury, dealt with foreign affairs, oversaw the construction of monumental buildings, and resolved legal disputes. They were considered the main link between the pharaoh and the populace, ensuring the smooth functioning of the state administration.
4. The Scribes: The Guardians of Knowledge
Scribes formed an essential part of the state administration in ancient Egypt. These highly skilled individuals were educated in reading, writing, and arithmetic to meticulously record events, maintain records, and document legal proceedings. They were responsible for keeping detailed accounts of the state's resources and transactions, enabling efficient governance.
Without scribes, the state machinery would have struggled to function smoothly, as their expertise allowed for accurate record-keeping, communication, and dissemination of knowledge. Their meticulous work also contributed to the preservation of ancient Egyptian history.
5. Temple Priests: Spiritual Guardians and Administrators
The temples of ancient Egypt were not only places of worship but also centers of administration and economic power. Temple priests held significant influence and were involved in various state activities. They managed vast estates, oversaw economic affairs, and collected taxes on behalf of the state. Additionally, they administered justice within temple grounds. Their efforts helped drive the economy and maintain social order.
The state in ancient Egypt was a well-organized machine, with rulers, administrators, and officials working together to ensure order, prosperity, and divine guidance. The pharaohs, as earthly gods, led the civilization with unparalleled authority, while viziers, scribes, and temple priests managed the day-to-day affairs of the empire.
By studying the state structure and administration of ancient Egypt, we gain valuable insights into the governance practices that allowed this remarkable civilization to flourish and survive for millennia. It is a testament to human innovation and the thirst for knowledge that such a sophisticated system existed thousands of years ago.
4.8 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 4520 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Word Wise | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 220 pages |
| X-Ray for textbooks | : | Enabled |
This book presents a new analysis of the organization, structure and changes of the pharaonic state through three millennia of its history. Moreno García sheds new light on this topic by bringing to bear recent developments in state theory and archaeology, especially comparative study of the structure of ancient states and empires. The role played by pharaonic Egypt in new studies often reiterates old views about the stability, conservatism and 'exceptionalism' of Egyptian kingship, which supposedly remained the same across the Bronze and Iron Ages.
Ancient Egypt shared many parallels with other Bronze and Iron Age societies as can be shown by an analysis of the structure of the state, of the limits of royal power, of the authority of local but neglected micro-powers (such as provincial potentates and wealthy non-elite),and of the circulation and control of wealth. Furthermore, Egypt experienced deep changes in its social, economic, political and territorial organization during its history, thus making the land of the pharaohs an ideal arena in which to test applications of models of governments and to define the dynamics that rule societies on the longue durée. When seen through these new perspectives, the pharaonic monarchies appear less exceptional than previously thought, and more dependent on the balance of power, on their capacity to control the kingdom's resources and on the changing geopolitical conditions of their time.

 Calvin Fisher
Calvin FisherThe Most Insightful and Liberating Experiences Found in...
When it comes to expanding our...

 D'Angelo Carter
D'Angelo CarterDax To The Max Imagination: Unlock the Power of...
Welcome to the world of Dax To...

 Chris Coleman
Chris ColemanThe Hidden Case of Ewan Forbes: Uncovering the Mystery...
Ewan Forbes: a...

 Morris Carter
Morris CarterWhen Newport Beat New Zealand: A Historic Rugby Upset
The rivalry between Newport and New Zealand...

 David Mitchell
David MitchellThe Soul of an Astronomer: Women of Spirit
Astronomy, the study of...

 Ethan Gray
Ethan GrayThe Military Origins Of The Republic 1763-1789
When we think about the birth of the...

 Guy Powell
Guy PowellRPO System for 10 and 11 Personnel: Durell Fain
When it comes to...

 Evan Hayes
Evan HayesMadness: The Ten Most Memorable NCAA Basketball Finals
College basketball fans eagerly await the...

 Jorge Amado
Jorge AmadoDiscover the Magic of Polish: English First 100 Words,...
Are you ready to embark on a linguistic...

 Shaun Nelson
Shaun NelsonUnlock the Secrets of Edwidge Danticat's Breath, Eyes,...
Are you delving into the world...

 Walt Whitman
Walt Whitman300 Years Liechtenstein: The Birth of Fish Out of Water...
Once upon a time, in the...

 Jaden Cox
Jaden CoxExploring the Legendary Surfers of Early Surfing in the...
Surfing, a sport...
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 Heath PowellThe Incredible Journey: A Comprehensive Look into the History of Sharlston...
Heath PowellThe Incredible Journey: A Comprehensive Look into the History of Sharlston... Billy PetersonFollow ·2.6k
Billy PetersonFollow ·2.6k Kelly BlairFollow ·7.6k
Kelly BlairFollow ·7.6k Gary CoxFollow ·16.7k
Gary CoxFollow ·16.7k Jarrett BlairFollow ·3.1k
Jarrett BlairFollow ·3.1k Langston HughesFollow ·13.3k
Langston HughesFollow ·13.3k Clayton HayesFollow ·13.8k
Clayton HayesFollow ·13.8k Dylan HayesFollow ·14.5k
Dylan HayesFollow ·14.5k Theo CoxFollow ·7.7k
Theo CoxFollow ·7.7k




















