















Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
The Remarkable History of Energy: From Ancient Fire to Modern Power

Energy has always been a fundamental part of human existence. From the discovery of fire by early humans to the development of nuclear power, the history of energy is a fascinating journey filled with innovation and progress. In this article, we will explore the remarkable timeline of energy development and its crucial role in shaping the world as we know it today.
Ancient Energy Sources
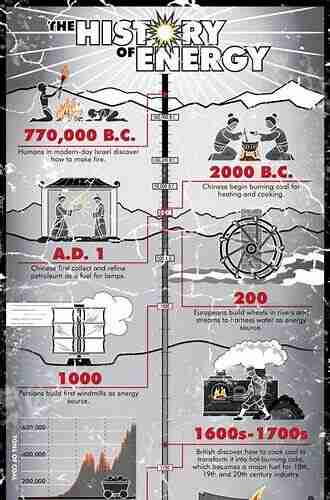
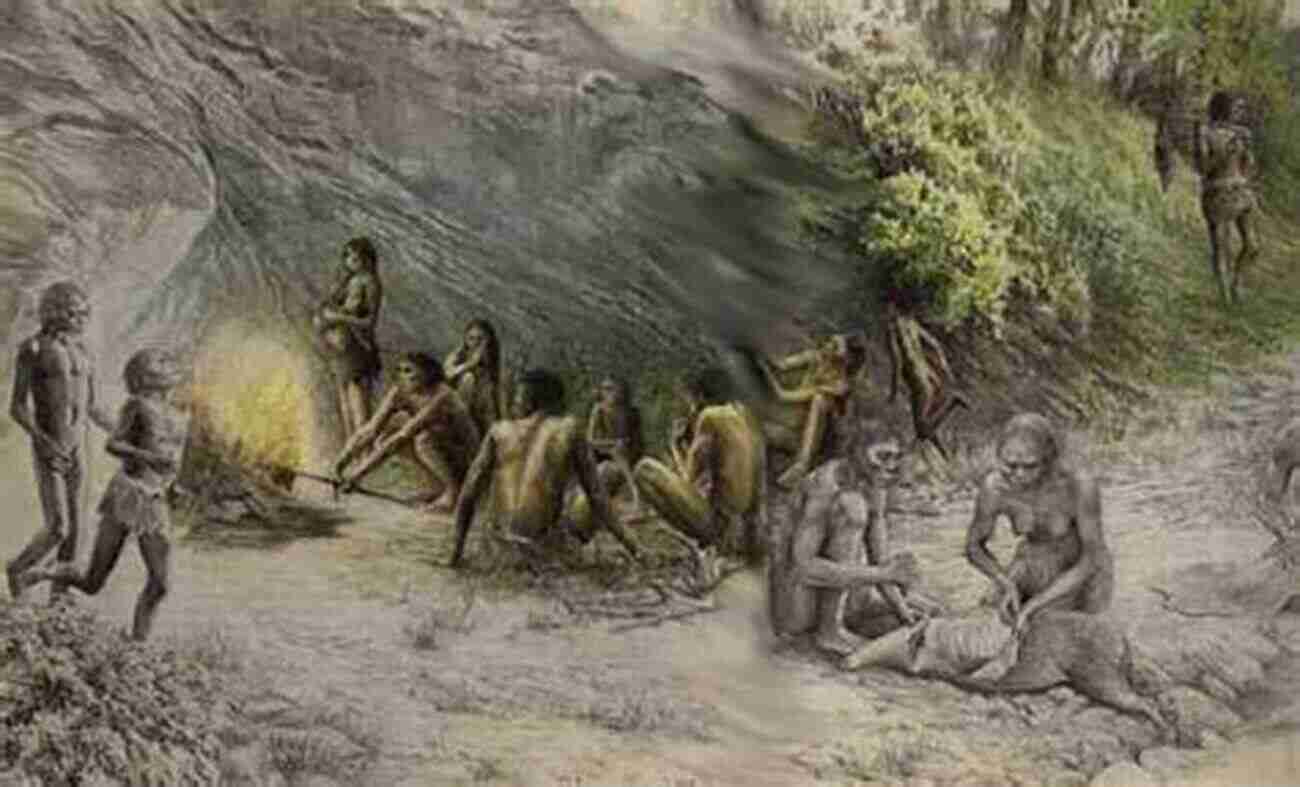
The earliest known energy source used by humans was fire. The ability to control and utilize fire revolutionized human civilization. It provided warmth, protection, and the ability to cook food. Fire was harnessed through the burning of wood, which was readily available in the surrounding environment.
Another significant energy source during ancient times was animal power. Domestication of animals like horses and oxen allowed humans to perform tasks such as plowing fields and transportation. This marked a significant shift towards mechanization and increased productivity.
4 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 52825 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Word Wise | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 552 pages |

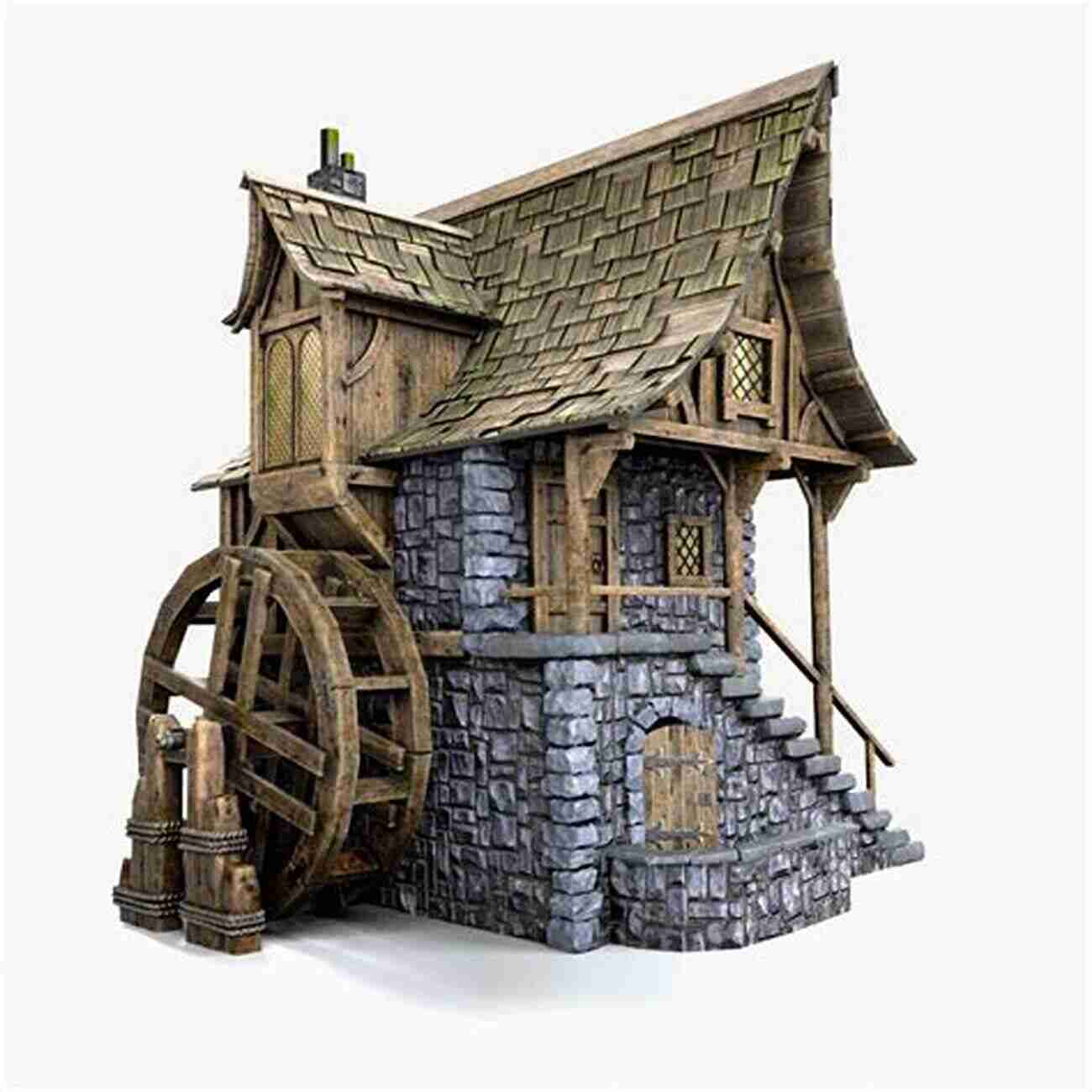
Medieval Period: Wind and Water Power
As societies progressed, they began harnessing the power of wind and water. Windmills emerged as a significant source of energy, providing mechanical power for activities such as grinding grains and pumping water. Watermills, on the other hand, utilized flowing or falling water to perform tasks like grinding flour and sawing wood.
These advancements in energy sources spurred industrial growth during the medieval period. They encouraged the development of industries such as textile production and milling. Furthermore, the usage of water and wind power led to the establishment of early manufacturing centers, shaping the foundation of modern cities.

The Industrial Revolution: Coal and Steam Power
The Industrial Revolution brought about a significant shift in energy sources. The invention of the steam engine by James Watt in the late 18th century marked a revolutionary breakthrough. Powered by coal, the steam engine provided a reliable and efficient source of energy, enabling the mechanization of factories and transportation systems.
Coal became the dominant energy source during this period. It was abundantly available and provided a high energy output. The mining and utilization of coal led to the growth of industries such as iron and steel production. The reliance on coal also fueled the expansion of railways and steamships, revolutionizing global trade and communication.
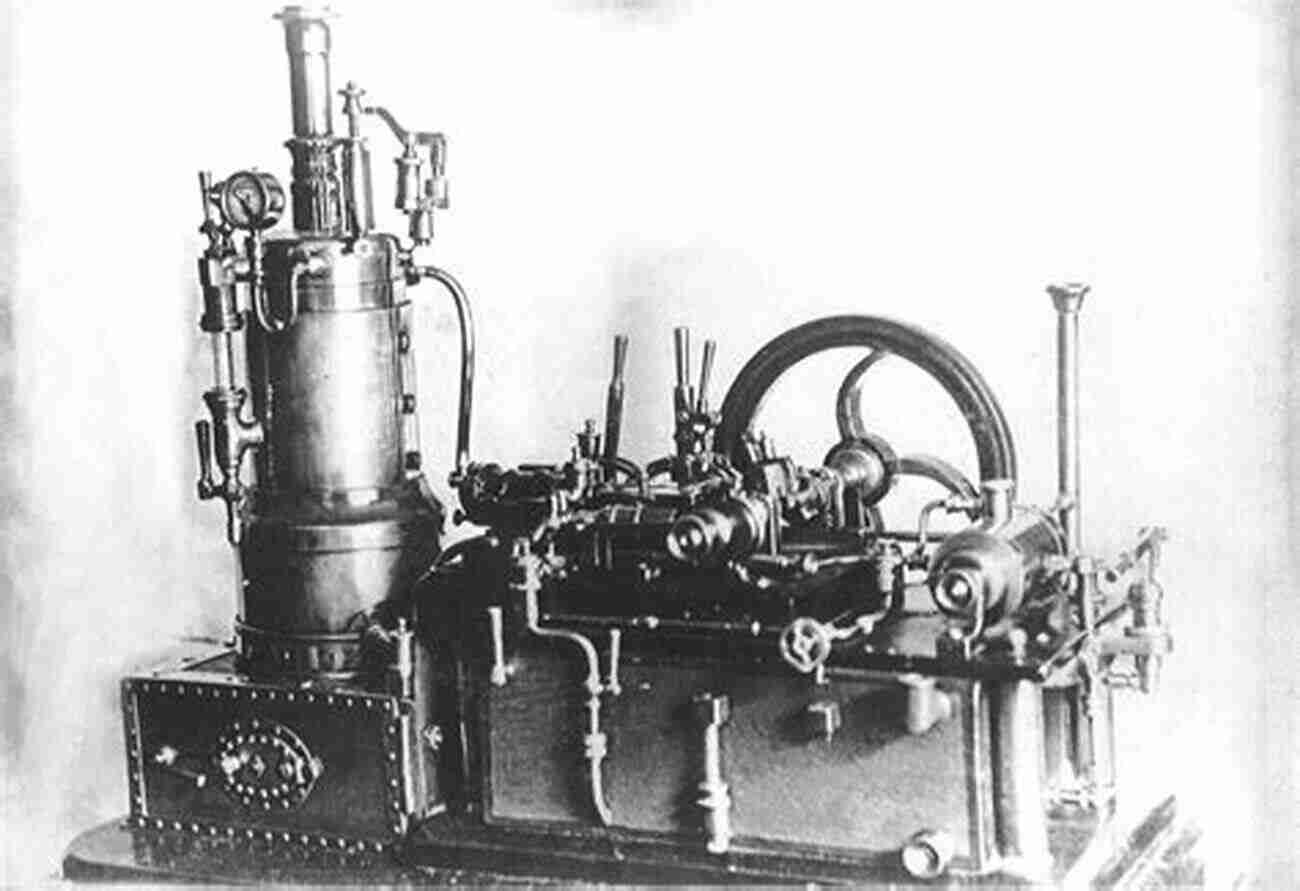
Electrification and Fossil Fuels
The late 19th and early 20th centuries witnessed the widespread adoption of electricity as a primary energy source. The discovery of the practical applications of electricity by inventors like Thomas Edison and Nikola Tesla transformed society. It led to the electrification of cities, homes, and industries.
Fossil fuels, particularly oil, also played a significant role during this period. The internal combustion engine, fueled by petroleum, revolutionized transportation. The invention of the automobile and subsequent developments in aviation propelled global connectivity and mobility.
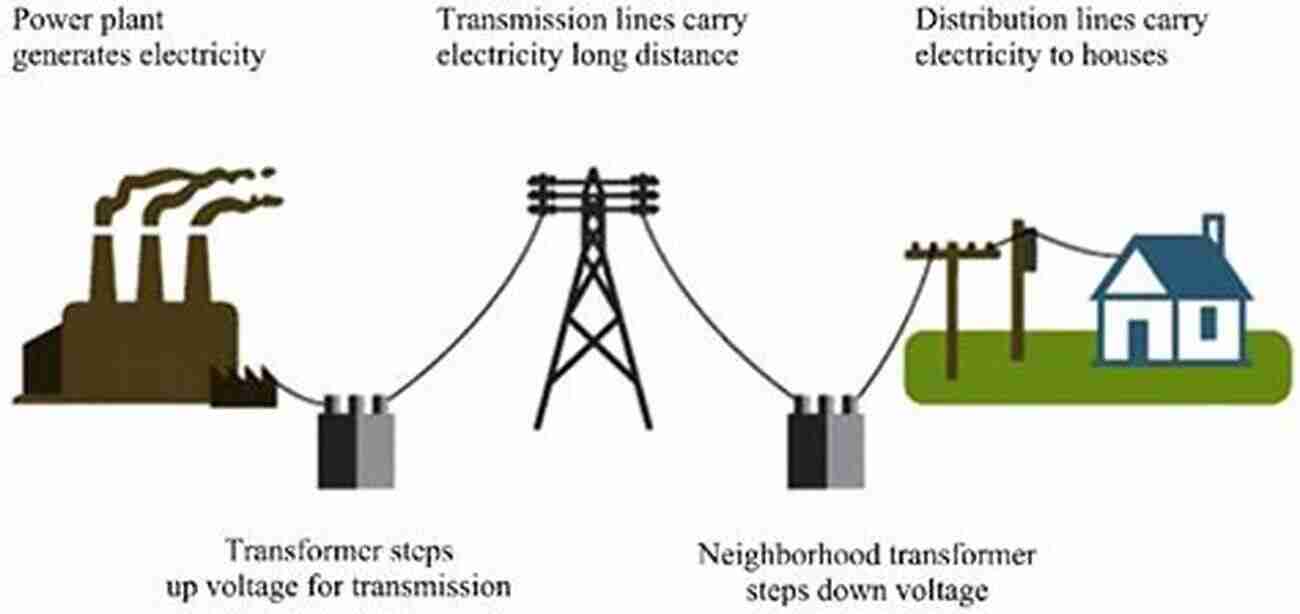
Modern Energy Era: Renewable Energy and Nuclear Power
In recent decades, there has been increasing concern about the environmental impact of traditional energy sources. This has led to a focus on renewable energy alternatives such as solar, wind, and hydropower. These sources have gained traction due to their sustainability and reduced carbon emissions.
Additionally, nuclear power has emerged as a controversial yet powerful energy source. Despite its potential for clean energy generation, there are inherent risks associated with nuclear technology, primarily due to the disposal of radioactive waste.
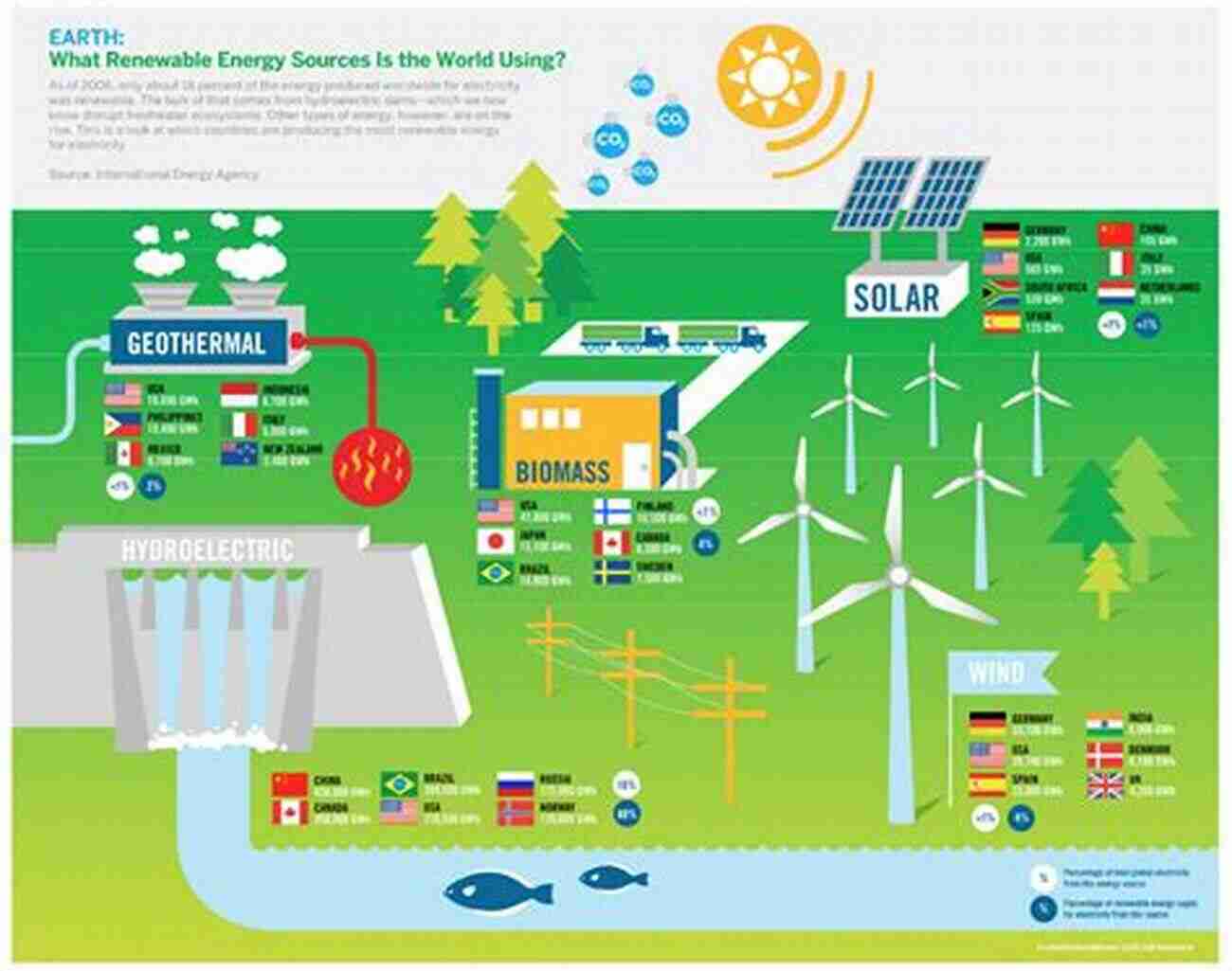
The Future of Energy
As we move forward, the future of energy is likely to involve a diversified mix of sources. The push for cleaner and more sustainable alternatives will continue to drive innovation in renewable energy technologies. Advancements in battery storage and smart grid systems will enable a more efficient and decentralized energy distribution system.
Moreover, the need to address climate change and reduce greenhouse gas emissions will likely steer the energy landscape towards greater reliance on renewable sources. This transition will require global collaborative efforts, policy changes, and investments in research and development.
The history of energy is a testament to humanity's ingenuity and resilience. From ancient fire to modern power systems, energy has remained an integral part of our progress. As we embrace the challenges of the future, it is essential to prioritize sustainable and innovative energy solutions that can power the world while preserving our planet.
4 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 52825 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Word Wise | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 552 pages |
In this seminal book, Bent Sørensen views human society as driven by the quest for, and control of, energy. From allowing our prehistoric ancestors to survive harsh northern European winters to more recent global energy security and climate concerns, the control and effective harnessing of energy sources has played a central role in human development. Using the written and archaeological record and, from earlier times, inferring the energy needs of humans through modeling of climatological conditions and other indirect parameters, Sørensen unwraps this previously little-explored field.
Based on detailed studies of northern Europe – and in particular the case of Denmark – the focus moves from the stone age, through the development of agriculture and trade, migration and exploration, medieval society and the renaissance, into industrial times and present-day debates around the transition to low-carbon forms of energy supply.
This riveting examination of a nascent field of study provides a new perspective for historians and those wishing to gain a deeper understanding of the background to present-day energy debates.

 Calvin Fisher
Calvin FisherThe Most Insightful and Liberating Experiences Found in...
When it comes to expanding our...

 D'Angelo Carter
D'Angelo CarterDax To The Max Imagination: Unlock the Power of...
Welcome to the world of Dax To...

 Chris Coleman
Chris ColemanThe Hidden Case of Ewan Forbes: Uncovering the Mystery...
Ewan Forbes: a...

 Morris Carter
Morris CarterWhen Newport Beat New Zealand: A Historic Rugby Upset
The rivalry between Newport and New Zealand...

 David Mitchell
David MitchellThe Soul of an Astronomer: Women of Spirit
Astronomy, the study of...

 Ethan Gray
Ethan GrayThe Military Origins Of The Republic 1763-1789
When we think about the birth of the...

 Guy Powell
Guy PowellRPO System for 10 and 11 Personnel: Durell Fain
When it comes to...

 Evan Hayes
Evan HayesMadness: The Ten Most Memorable NCAA Basketball Finals
College basketball fans eagerly await the...

 Jorge Amado
Jorge AmadoDiscover the Magic of Polish: English First 100 Words,...
Are you ready to embark on a linguistic...

 Shaun Nelson
Shaun NelsonUnlock the Secrets of Edwidge Danticat's Breath, Eyes,...
Are you delving into the world...

 Walt Whitman
Walt Whitman300 Years Liechtenstein: The Birth of Fish Out of Water...
Once upon a time, in the...

 Jaden Cox
Jaden CoxExploring the Legendary Surfers of Early Surfing in the...
Surfing, a sport...
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 Preston SimmonsUnleash Your Sports Skills: Mastering Basketball, Association Football,...
Preston SimmonsUnleash Your Sports Skills: Mastering Basketball, Association Football,... Richard WrightFollow ·4k
Richard WrightFollow ·4k José SaramagoFollow ·11.3k
José SaramagoFollow ·11.3k Robbie CarterFollow ·18.6k
Robbie CarterFollow ·18.6k Luke BlairFollow ·12k
Luke BlairFollow ·12k James HayesFollow ·15k
James HayesFollow ·15k Eugene ScottFollow ·5.6k
Eugene ScottFollow ·5.6k Tyler NelsonFollow ·8.7k
Tyler NelsonFollow ·8.7k Branson CarterFollow ·6.4k
Branson CarterFollow ·6.4k